Early Detection of the ‘Cheating Gene’ to Protect Family Happiness

Recently, scientists around the world have made a surprising discovery regarding the so-called "cheating gene."
This revelation has led to intriguing speculation: Could our genes determine whether we choose loyalty or betrayal? Can genetic testing predict whether someone is prone to infidelity?
These questions have sparked discussions about human nature, morality, and intimate relationships. This article delves into the details of the “cheating gene” uncovered by the latest scientific research and explores its profound impact on married life.
Infidelity is not uncommon in human society. It refers to a married person engaging in inappropriate relations with someone outside the marriage, breaking the bond of fidelity and marital commitment. Human infidelity can be explained through various lenses, including biology, psychology, and sociology.
From a biological perspective, infidelity is not entirely random. In the course of human evolution, the instinct to pass on one’s genes has driven individuals to select optimal mates.
This reproductive strategy causes people to seek partners with greater genetic advantages, which may lead to infidelity. Human sexual behavior is also influenced by hormones—fluctuations in hormone levels can increase intimacy and lead to unfaithfulness.
Psychologically, infidelity can result from emotional dissatisfaction within a marriage or long-term relationship. As relationships progress, passion often fades, novelty diminishes, and unresolved conflicts may increase tension between partners.
When emotional needs are unmet, individuals may be tempted to seek comfort or excitement elsewhere. Curiosity, the desire for adventure, and a craving for new experiences also contribute to unfaithfulness.
Sociologically, cultural values influence deviant behavior, including infidelity. Different cultures have varied perceptions and norms surrounding marriage and fidelity.
In some societies, male infidelity may be viewed as a symbol of charm or social status, while in others, female infidelity is harshly condemned as immoral or disloyal.
Modern society presents numerous temptations—workplace flirtations, attention from the opposite sex, and more—that can challenge personal loyalty.
To minimize infidelity, both individuals and society must work to strengthen marital and family relationships. Emotional communication, mutual trust, and respect between spouses are vital. Additionally, legal systems and ethical standards should continue evolving to discourage infidelity.
Ultimately, infidelity results from a combination of factors. Biology, psychology, and sociology all offer valid explanations. By understanding the root causes of infidelity, individuals and society can better manage relationships, contributing to family stability and harmony.
The discovery of genes linked to infidelity provides a new perspective on the genetic basis of human behavior. Some believe environment solely shapes our actions, while others argue that genetics play a significant role.
This research offers strong evidence supporting the influence of genes in shaping behavior. It marks a meaningful step forward in understanding the mechanisms behind human actions and can help inform mental health management and social education.
Genetic testing may one day help predict a person’s potential risk of infidelity. With this insight, targeted interventions—such as psychological counseling—could reduce infidelity rates, helping preserve family unity.
Armed with scientific insights, we can design better treatment and support plans, including psychological therapy and behavioral interventions. These measures can help individuals struggling with infidelity rebuild themselves and strengthen their relationships.
News in the same category


Don't take too much of it because you'll become the alpha male of all women 💥

Cheesecake Tart Recipe (Cream Cheese Tart)

Stop buying these at the store. 8 homemade frostings you can make at home

Here's the 1 main reason you should never eat ramen noodles, according to studies

No Diet Needed – Just One Cup a Day and Say Goodbye to Stubborn FAT!

12 Delicious and Nourishing Hot Chocolate Recipes

Food Pairings That Make or Break Your Meals: 25 Combinations You Should Know

Are You Eating at the Right Time? Why When You Eat Matters as Much as What You Eat

8 Diabetes-Friendly Snacks That Won’t Spike Blood Sugar

Roasted Beets (How To Roast Beets)

Greek Chickpea Salad + Tzatziki Dressing

Blackened Salmon Stuffed with Spinach & Parmesan

🍽️ Creamy Chicken, Mushroom & Asparagus Penne – The Ultimate Comfort Pasta! 🍄🥦🍗

My Kidneys Were in Danger – Here’s What I Took! In Less Than 5 Minutes, You’ll Have the Solution – Try It and Heal Your Kidneys for Life!

Did You Know That Coconut Water Can Unclog Veins, Eliminate Kidney Stones, and Even Help with Diabetes and Asthma?
The Nightly Benefits of Eating Raw Garlic Before Bed

Citrus Banana Bliss: A 5-Minute No-Bake Delight 🍌🍊
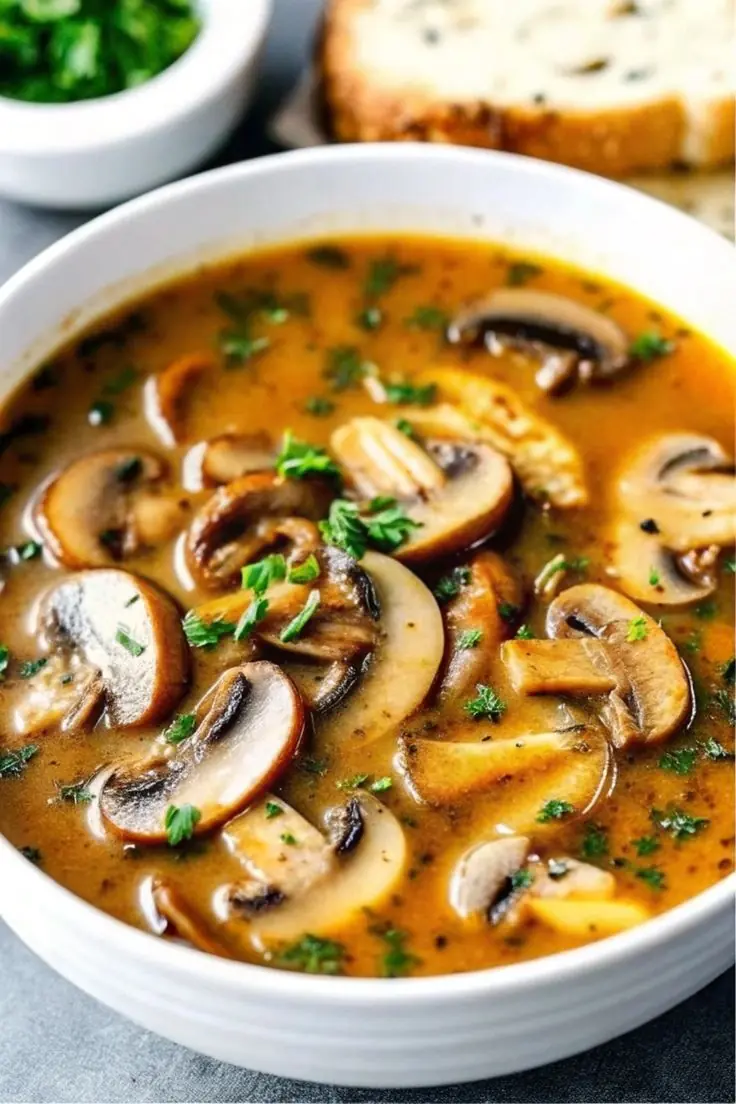

Rotisserie Chicken Mushroom Soup: A Creamy, Comforting Delight! 🍗🍄
News Post

Mix Baking Soda with Lemon: 8 Surprising Benefits Every Woman Should Know

The Best Morning and Evening Tea: 6 Health Benefits of Garlic, Turmeric, Onion, Ginger, Cinnamon, and Guava Leaf for Seniors
High Cholesterol Symptoms (and High Triglycerides)

Papaya Seeds: Health Benefits and How to Use Them

Benefits of olive oil 😱😱

10 top natural painkillers

Homemade Anti-Wrinkle Cream with Nivea, Coconut Oil, and Cornstarch

Doctor Reveals: Mix Banana Peel with Cinnamon and Cloves

PINEAPPLE – A NATURAL REMEDY FOR STROKE PREVENTION & LIVER-KIDNEY DETOX

This 2025 Herbal Elixir Is Emptying Hospitals—What’s Behind the Craze?

Homemade Butter Pecan Ice Cream

At 63 Years Old, I Eliminated Poor Circulation, Diabetes, Swollen Feet, and Even Cancer

Peppermint (Mint) and Rosemary: A Powerful Herbal Infusion for Wellness
Fatty Liver Disease: 6 Silent Warning Signs You Shouldn't Ignore 👇👇

Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum): A Powerful Medicinal Herb for Liver Health and More
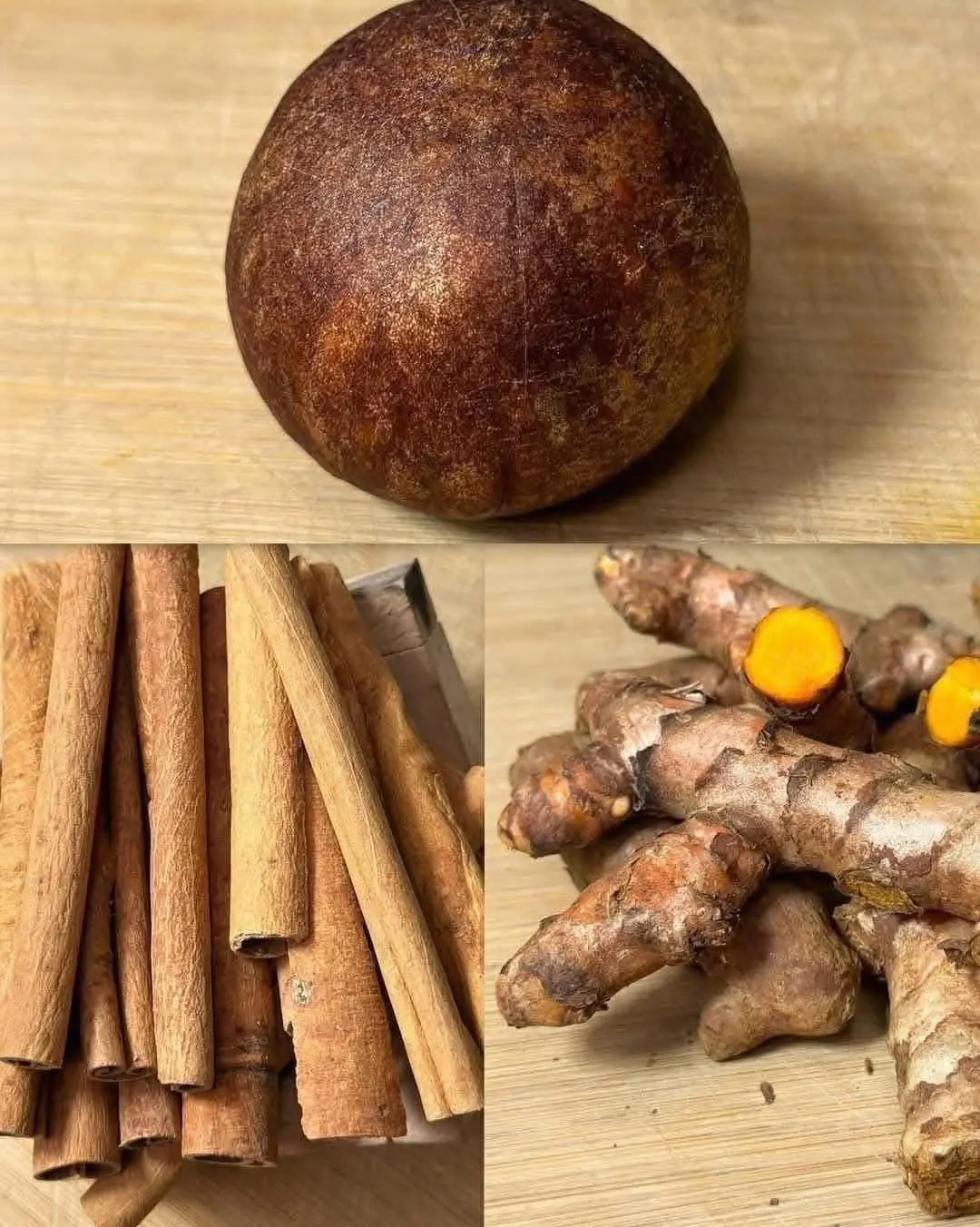

Drink avocado seed tea with turmeric and cinnamon 🥑
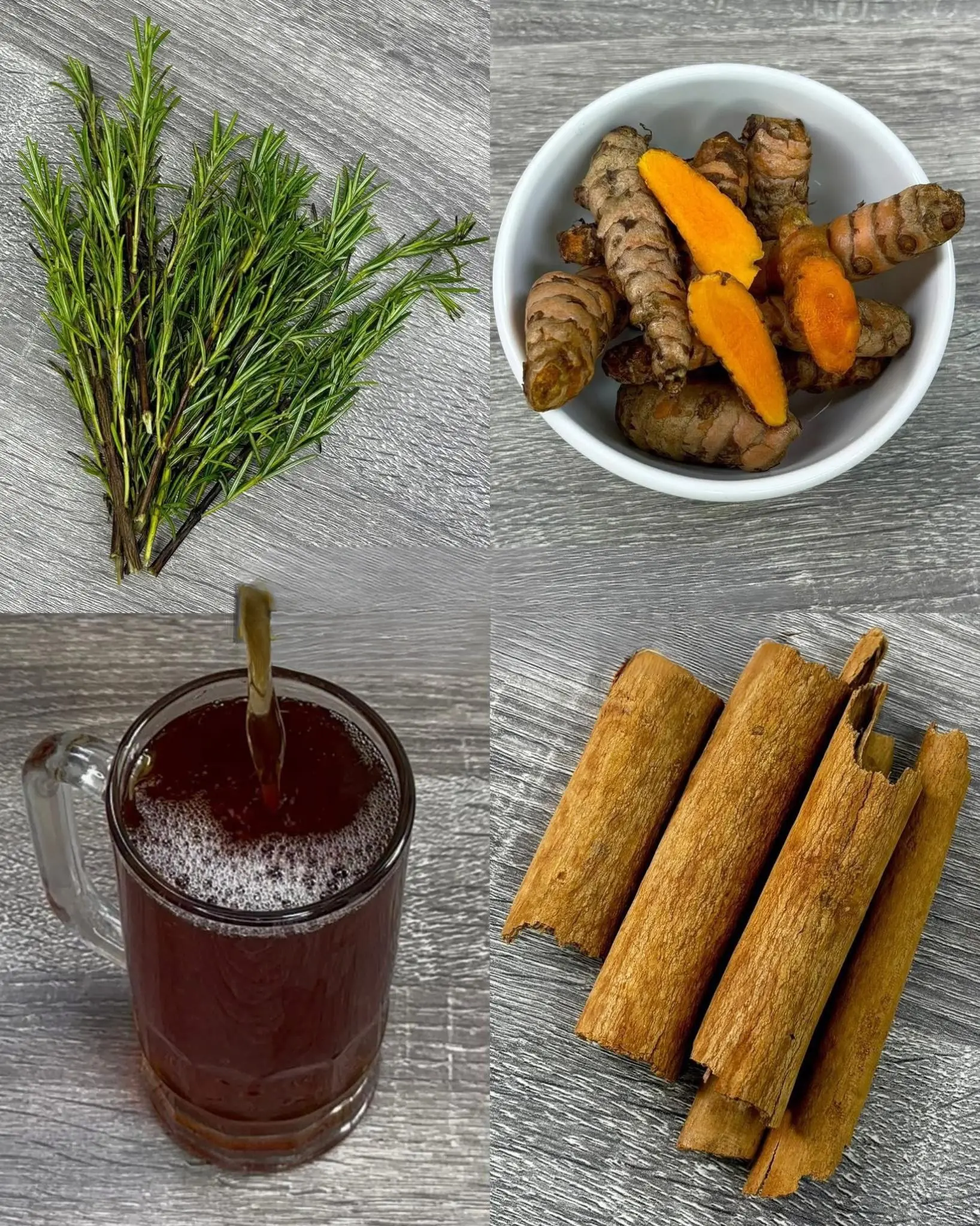

They Call It the “Blood Sugar Remover” – A Natural Remedy Passed Down for Over 100 Years
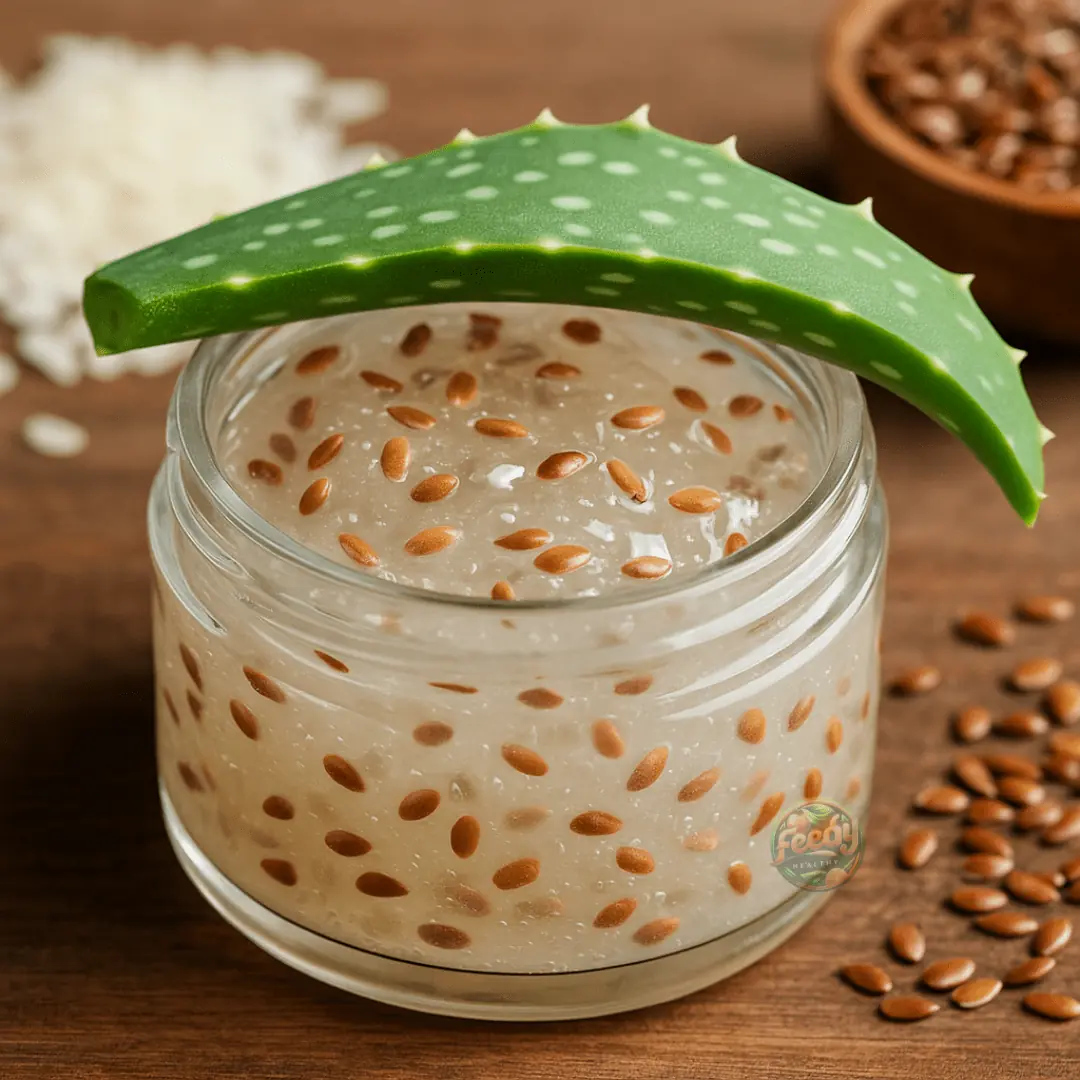

Rice Flaxseed Gel For Youthful & Glowing Skin

11 AM – THE GOLDEN HOUR WHEN YOUR BLOOD FAT AND BLOOD PRESSURE WILL “BE GRATEFUL” IF YOU REMEMBER TO DO THIS ONE SIMPLE THING…
